STAY INFORMED
following content serves as a personal note and may lack complete accuracy or
certainty.
Minimal-Mistakes instruction
Useful vscode Shortcut Keys
Git Note
PHP Form
Heredoc
Heredoc is a syntax feature that allows for the creation of strings that span multiple lines without the need for explicit concatenation or special escape characters. It’s particularly useful for writing large blocks of text, such as HTML or SQL queries, within PHP code.
header, footer using heredoc
function headerHTML($title = ""){
echo <<<HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>$title</title>
</head>
<body>
HTML;
}
function footerHTML(){
echo<<<HTML
</body>
</html>
HTML;
}
Form
POST
function formPrac(){
if ('POST' == $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']){
echo 'Hello ' . $_POST['name'];
}
else{
echo <<<HTML
<form method="POST" action="">
<input type="text" name='name'>
<input type="submit" name='submit' value='Submit'>
</form>
HTML;
}
}
formPrac();
When submit input is clicked, the form data will be sent to the same page (since the action attribute is empty action=””) using the POST method.
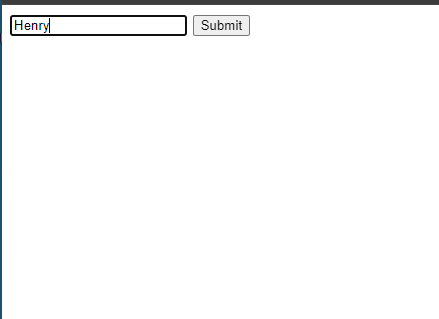

Auto-Global Arrays
At every request, the PHP engine sets up some auto-global arrays that contain the values of parameters submitted in a form or passed in the URL.
function formPrac($errors = []){
if ('POST' == $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']){
echo 'You have chosen ' . $_POST['menu'];
}
else{
echo <<<HTML
<form method="GET" action="">
<select name="menu">
<option value="beef">Beef</option>
<option value="chicken">Chicken</option>
<option value="pork">Pork</option>
</select>
<input type="submit" name='submit' value='Submit'>
</form>
HTML;
}
}
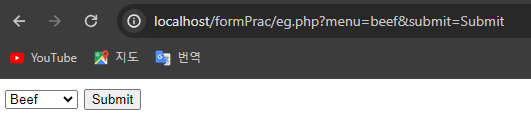
If the method is POST,

Element with Multiple Values
A form element with multiple values its name must end with [].
function formPrac($errors = []){
if ('POST' == $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']){
if (isset($_POST['menu'])){
foreach ($_POST['menu'] as $menu){
echo "You have chosen $menu.<br/>";
}
}
}
else{
echo <<<HTML
<form method="POST" action="">
<select name="menu[]" multiple>
<option value="beef">Beef</option>
<option value="chicken">Chicken</option>
<option value="pork">Pork</option>
</select>
<input type="submit" name='submit' value='Submit'>
</form>
HTML;
}
}
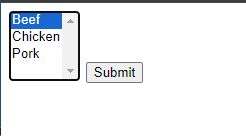

If the form above is submitted with 2 values selected, then $_POST[‘menu’] becomes a two-element array.

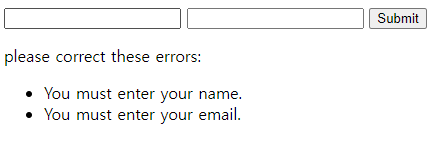
Validate Form
// define default argument is empty array
function showForm($errors = []){
echo <<<HTML
<form method="POST" action="">
<input type="text" name='name'>
<input type="email" name='email'>
<input type="submit" name='submit' value='Submit'>
</form>
HTML;
// if $errors is not empty,
if ($errors){
print 'please correct these errors: <ul><li>';
print implode('</li><li>', $errors);
print '</li></ul>';
}
}
// it will return $errors array.
function validateForm(){
$errors = array();
// use trim() to remove leading and trailing whitespaces.
if (strlen(trim($_POST['name'] < 2))){
$errors[] = 'You must enter your name.';
}
if (strlen(trim($_POST['email'] < 2))){
$errors[] = 'You must enter your email.';
}
return $errors;
}
// when validation fails, you should explain the error to the user, if appropriate, redisplay the errornous value.
entered in the form element
function formPrac(){
if ('POST' == $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']){
if ($errors = validateForm()){
showForm($errors);
}
else{
echo "Hello $_POST[name], your email is $_POST[email]";
}
}
else{
showForm();
}
}
formPrac();
filter_input()
Use filter_input() function with an appropriate filter, to check for numeric of string.
$check = filter_input(INPUT_POST, 'name', FILTER_VALIDATE_STRING);
if (is_null($check) || ($check) === false){
$errors[] = 'Please enter valid name';
}
- If the specified input element is valid, filter_input() returns the value.
- If the specified input element is missing, it returns null.
- If the specified input element is invalid, it returns false.
Comprehensive Validation
function validateForm(){
$errors = array();
$input = array();
$input['name'] = filter_input(INPUT_POST, 'name', FILTER_VALIDATE_STRING);
if (is_null($input['name']) || $input['name'] === false){
$errors[] = 'Please enter valid name.';
}
return array($errors, $input);
}
// more readable
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == 'POST'){
list($formError, $input) = validateForm();
.
.
.
}
Number Range
$input['number'] = filter_input(INPUT_POST, 'number', FILTER_VALIDATE_INT,
array('options' => array('min_range' => 18, 'max_range' => 65)))
// FILTER_VALIDATE_FLOAT filter doesn’t support the min_range and max_range options
$input['float'] = filter_input(INPUT_POST, 'number', FILTER_VALIDATE_FLOAT);
if (is_null($input['float']) || ($input['float'] === false) || ($input['float'] < 10.00) || ($input['float']) > 50.00){
$errors[] = 'please enter a valid price between $10 and $50.';
}
Select Menu
$menus = array('Beef', 'Chicken', 'Pork');
function generateMenu($options){
$html = '';
foreach ($options as $option){
$html .= "<option>$option</option>\n";
}
return $html;
}
function showForm(){
$menu = generateMenu($GLOBALS['menus']);
echo <<<HTML
<form method='POST'>
Your Order:
<select name='order'>
$menu
</select>
<input type="submit" value='Order'>
</form>
HTML;
}
Validate Select
$input['menu'] = $_POST['menu'];
if (!in_array($input['menu'], $GLOBALS['menus'])){
$errors[] = 'Please choose a valid menu';
}
HTML Entities
Submitted form data that contains HTML or JavaScript can cause big problems. Use strip_tags() to remove HTML tags from an input data.
// remove HTML from comment. It removes such as <b>, <div> and so on.
$comment = strip_tags($_POST['comment']);